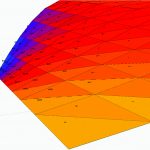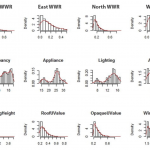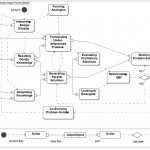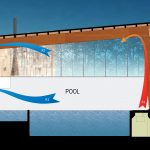
The natatorium environment is one of the most challenging environments to design and build in northern climates. This is due to the large swings in levels of humidity and temperature between interior and exterior conditions. The challenge remains how to balance the interior pool environment, requiring a consistent temperature and humidity level with the exterior; while taking into... Read more »